Electrical transformer symbols are essential for creating proper electrical plans. Without them, there’s no way to signify the type of transformer in a circuit. The different symbols specify many transformers, from single-phase to poly-phase. This is why it is crucial to know exactly which symbol you’re choosing.
Selecting the appropriate symbol helps avoid problems with power output and input. The function of transformers is to move energy between circuits. They also ensure uniformity between layouts.
Understanding these factors makes professional diagrams simpler to understand. With the help of this guide, you’ll learn how to use electrical transformer symbols and read circuit diagrams.
In this article
8 Common Transformer Symbols
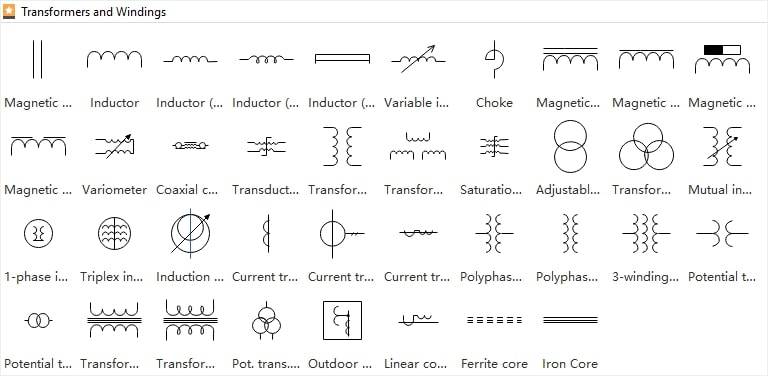
Transformer symbols in electrical diagrams may seem like tiny sketches, but they carry a lot of meaning. They indicate the type of transformer being used and its intended purpose. Whether it’s boosting voltage to send electricity across long distances or lowering it to make it safe for use in homes.
These symbols aren’t just for show. They help engineers understand how everything connects. It also illustrates how the real circuit will function before any actual parts are added. These symbols basically act as a blueprint before building the plan.
With new advancements every day, the electrical system plans are upgrading. Knowing what each symbol means becomes even more important. Before learning about the many types of transformer symbols, let’s go over some electrical symbols to set our basics straight.
| Schematic Symbol | Symbol Identification | Description |
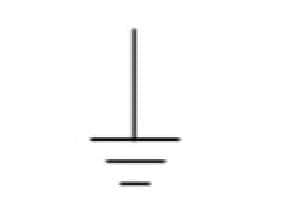 |
Ground or Earth | This symbol identifies a ground terminal from which the current is measured. Earth is used to show electrical shock protection. |
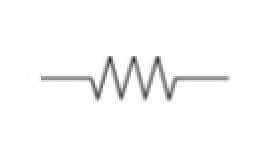 |
Resistor | A resistor is used to reduce or balance current flow. |
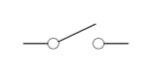 |
Switch | An open switch creates an open circuit. |
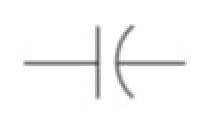 |
Capacitor | In this symbol, two terminals are visible. One is curved while the other is straight. This indicates a Polarized Capacitor. That means it should be connected in the correct order in the circuit for it to work as intended. |
 |
Fuse | A fuse is a special device that protects the circuit from an overflow of current. It does so by melting a wire present inside. |
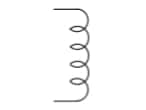 |
Inductor | This symbol looks like a series of repetitive coils. These inductor coils store energy when in a magnetic flux. An inductor is also known as simply ‘coil’ or ‘reactor’. |
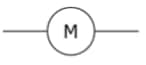 |
Motor | It transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. The motor is most crucial for any electronic appliance to work. |
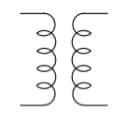 |
Transformer | A transformer helps balance the frequency of current in a circuit. Its structure consists of coils (two or more) coupled by magnetic induction. A real transformer also has a common iron core. |
Now that the basics are out of the way, here’s a breakdown of the most common symbols for transformers.
1.Single-Phase Transformer
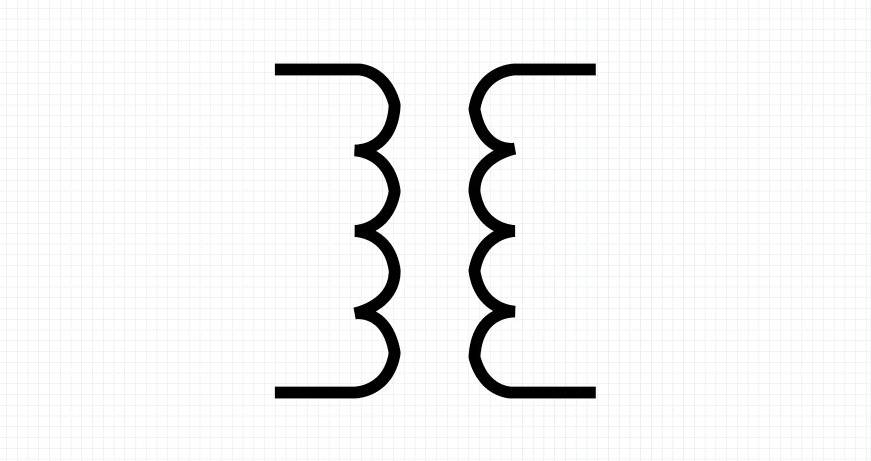
A single-phase transformer is a device operating on single-phase power. The term single–phase power refers to an alternating current (AC) power system. These types of systems are commonly found in residential or low-voltage settings.
The components of a single-phase transformer consist of a magnetic iron core and copper windings. The windings are properly insulated to avoid electrical faults and mishaps.
2.Polyphase Transformer
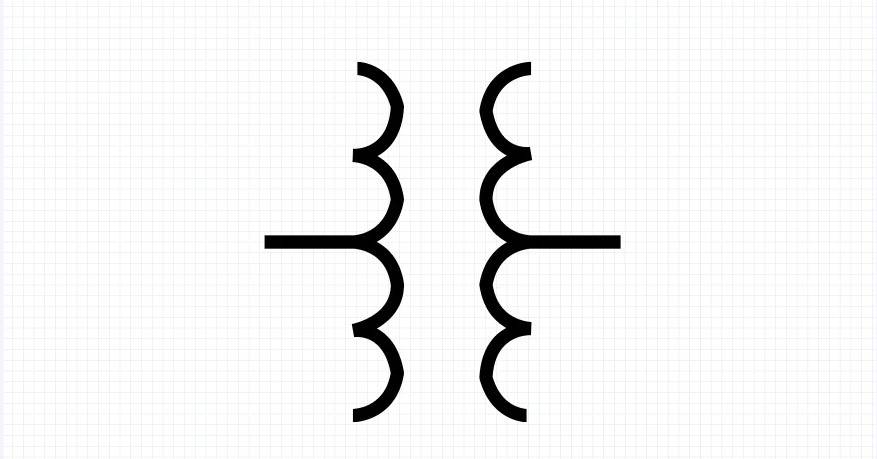
Polyphase transformers are the most common types. These are found in generators and factories as they’re designed to power large machines. A polyphase transformer works with three-phase power, which is the backbone of most industrial electrical systems.
Instead of a single wire, it uses three separate ones connected in a star (Y) or delta (Δ) configuration. This makes power transmission more efficient with less loss over long distances.
3.Adjustable Transformer
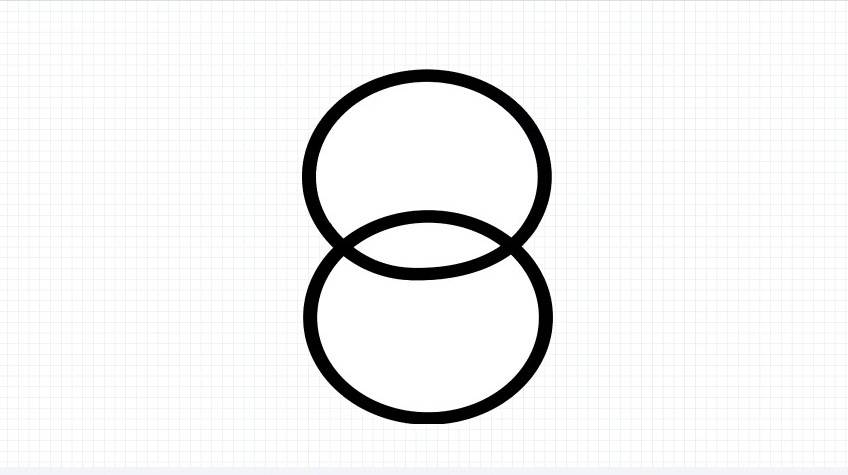
Adjustable transformer, also known as a Variac, works using a single coil where a movable brush changes the output level. It gets its name from “variable alternating current”. Think of it like a dial for voltage; you turn it up or down as needed.
These transformers are super useful in testing labs, motor speed controls, and light dimmers. They’re simple, but incredibly handy for precision.
4.Current Transformer
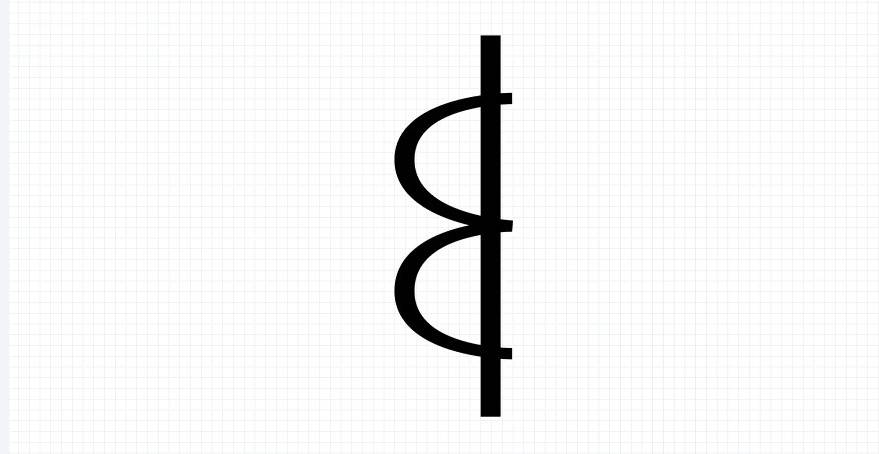
A current transformer is like a translator for high currents. It takes large, often dangerous levels of current coming from a power system. It then brings it down to a level that meters and home devices can safely handle. The cool part? It does so while keeping the current proportions intact. Current transformers are a must in substations to monitor electricity flow without putting anyone at risk.
5.Three-Winding Transformer
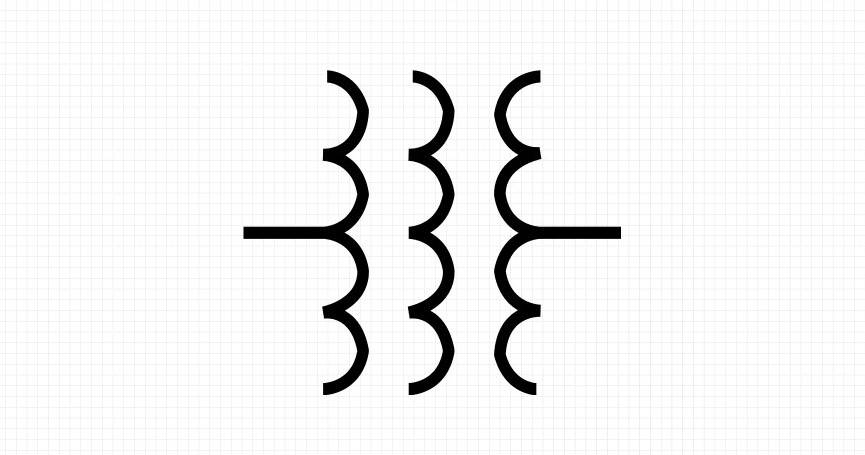
As the name suggests, this transformer has three sets of windings: one primary and two secondary. The three-winding transformer is perfect for an electrical system that supplies power at two different voltages. Think of it as a multitasker in power distribution systems.
These transformers can be found in substations. There, they help balance loads and optimize energy flow. It saves space, cost, and adds flexibility to electrical setups.
6.Saturation Transformer
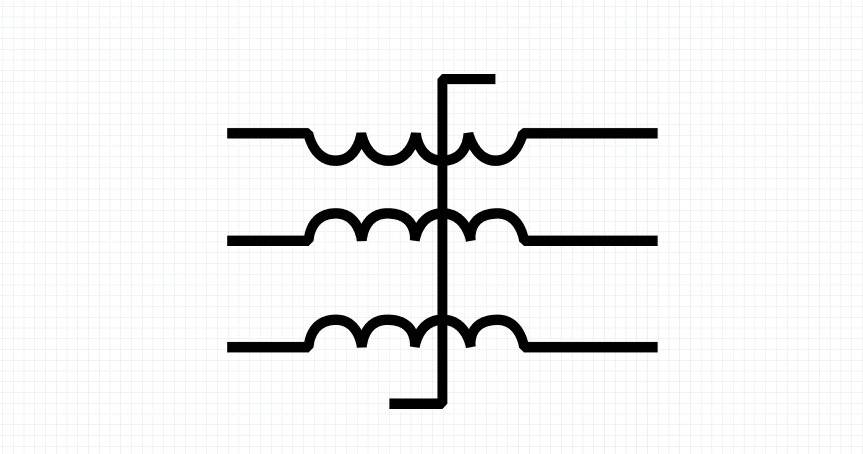
Saturation transformers are unique in their making. As their name suggests, they intentionally reach magnetic saturation at a specific point. This is done to limit current spikes in special circuits. Magnetic saturation means that once the current goes beyond a set level, it stops rising smoothly. This makes the transformer act as a safety buffer.
The behavior is non-linear on purpose, which can sound odd. However, in certain setups, it is necessary. This includes locating loads, waveform control, voltage regulation, and shaping.
7.Potential Transformer
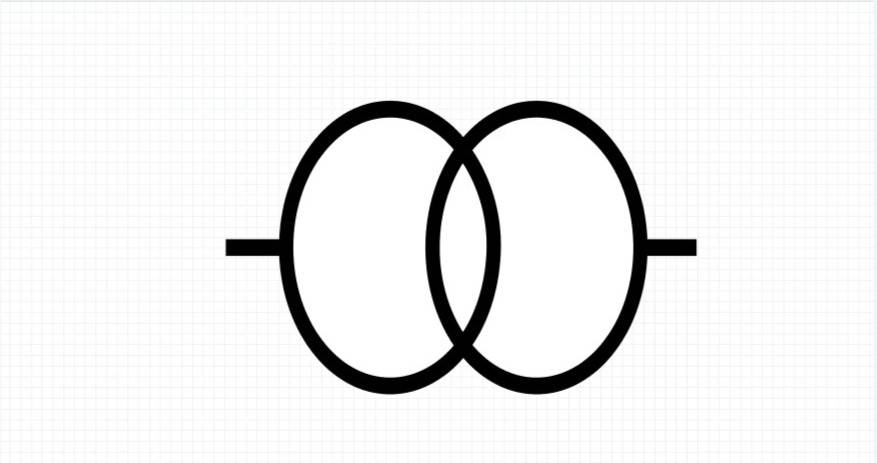
The potential transformer does for voltage what a current transformer does for current. It steps down to safer levels for measurement and protection. It’s built to keep voltage ratios accurate and signals in phase.
They can be found in high-voltage stations where monitoring is essential. Potential transformers let electricians measure voltages safely without hooking instruments to live high-voltage lines, which can be dangerous.
8.Shielded Transformer
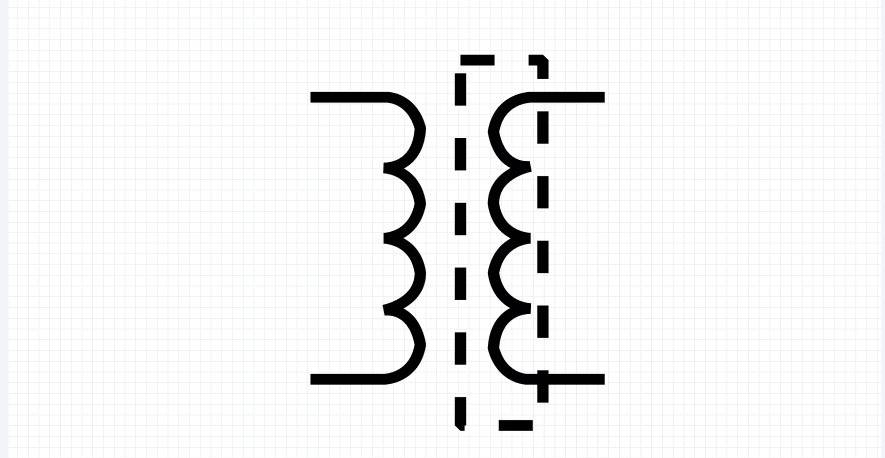
A shielded transformer has an extra electrostatic layer between its windings. This thin shield helps block electrical noise and reduce interference. Think of it like noise-cancelling headphones but for circuits. The shield also keeps unwanted signals at bay. It’s a go-to choice when clean, stable power is needed. They’re most common in sensitive tools, especially in medical equipment.
How to Create an Electrical Drawing on EdrawMax?
To truly utilize electrical transformer symbols, you need to create an electrical drawing. Don’t worry, you don’t have to be an electrical engineer to know how to do that.
With EdrawMax, a smart app, you can make professional diagrams with little to no experience. It contains ready-made templates of electrical plans and drawings. Just pick your template of choice, be it a home electrical plan or a power station. With its drag-and-drop interface, you can add whatever symbol you want to your plan and customize it with accessibility.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the steps to create an electrical drawing on EdrawMax.
Step1 Launch EdrawMax
- Download and install EdrawMax on your device.
- Once downloaded, launch EdrawMax with your login credentials.
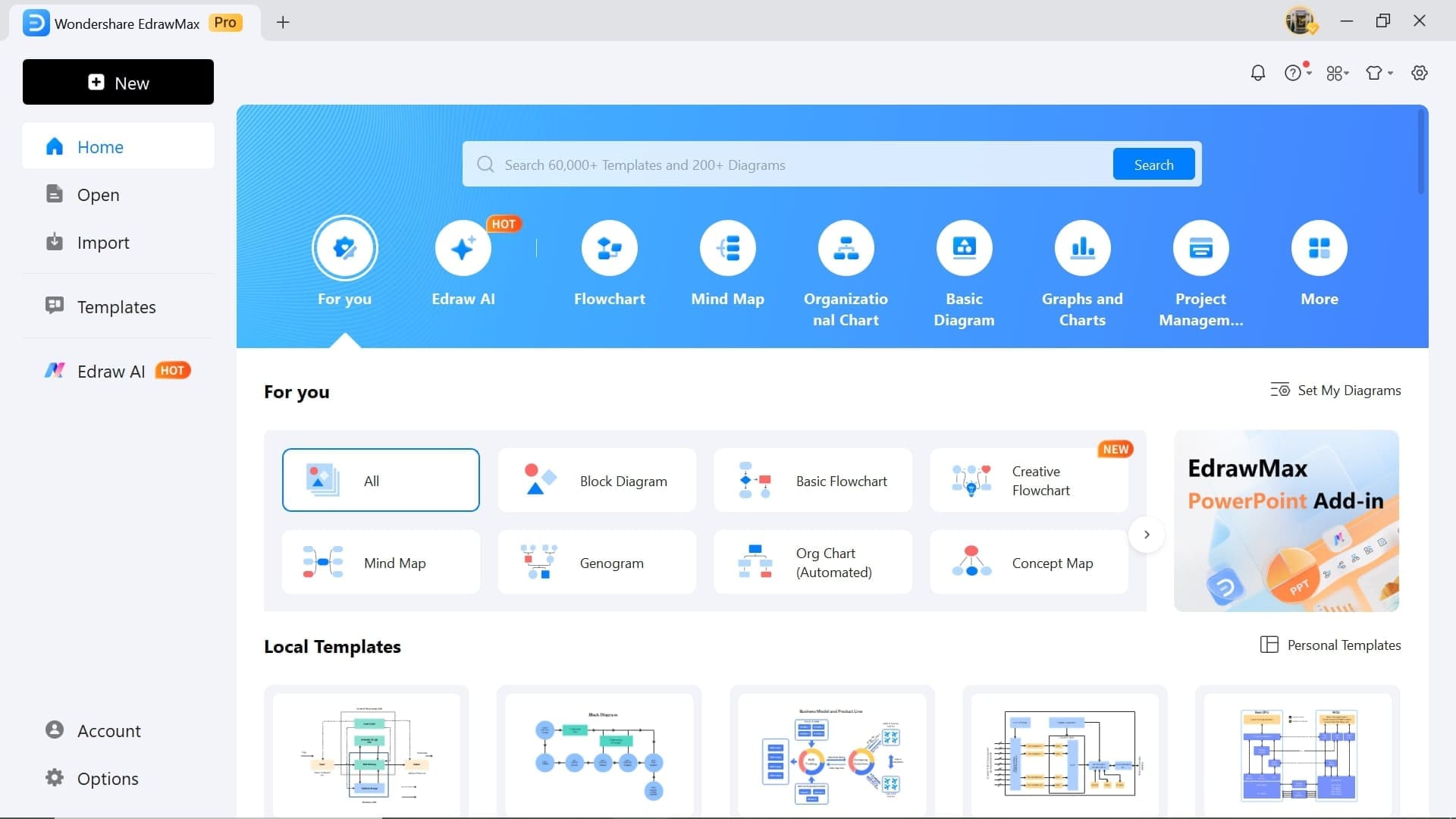
Step2 Select a New Template
- Once on the homepage, head to the Templates tab.
- Search Electrical Plan Drawing and hit Enter.
- Choose from the vast range of templates and click Use Immediately.
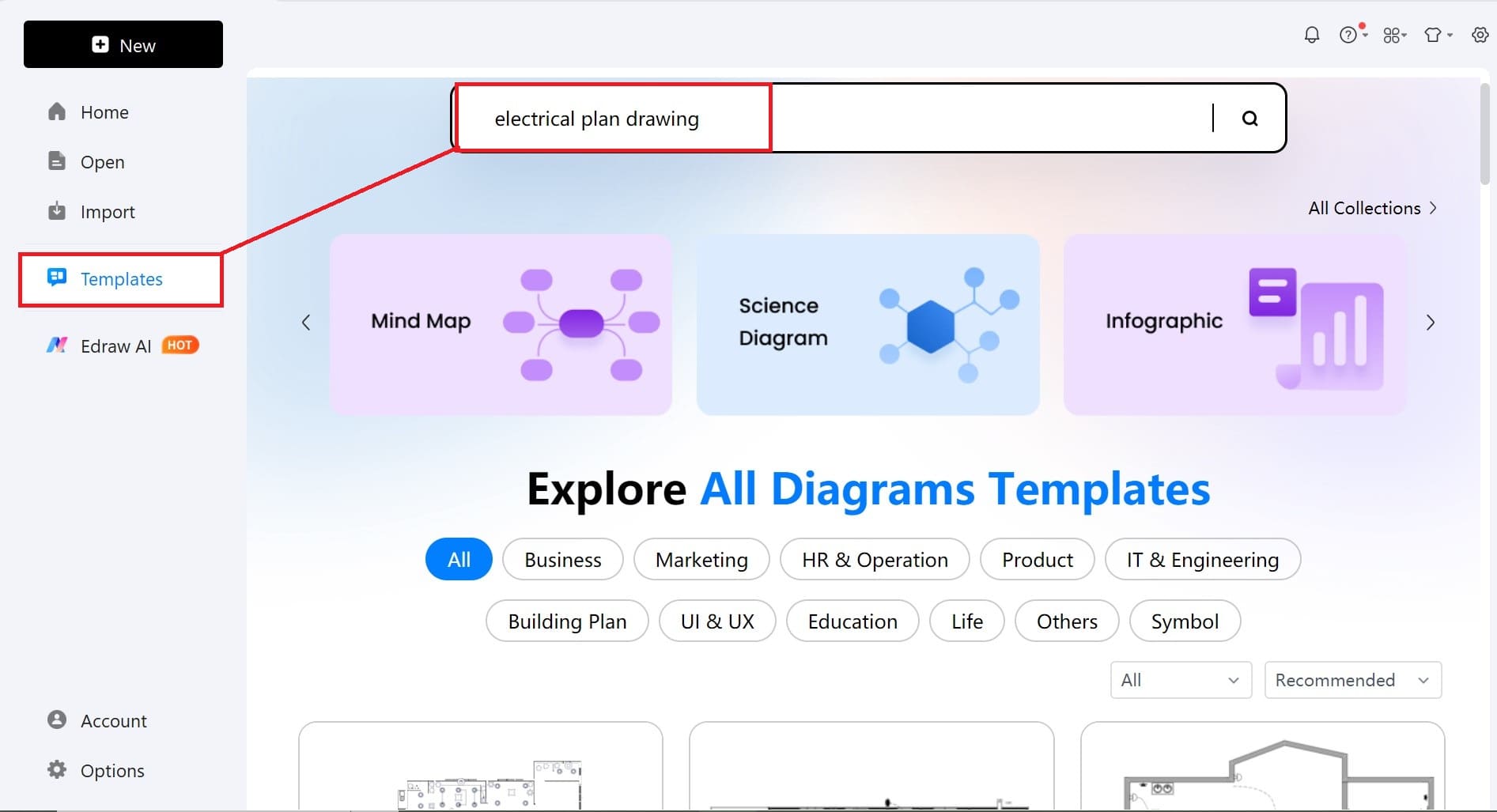
Step3 Start Customizing
- The template opens automatically on the editing canvas.
- Once there, have a look at your template. Make whatever changes you want in your plan.
- Change the colors with the bottom colors tab.
- Double-tap on any area where you want to add text.
- To customize the drawing lines, navigate to the right-hand panel.
- Change the positions and resize the components wherever necessary.
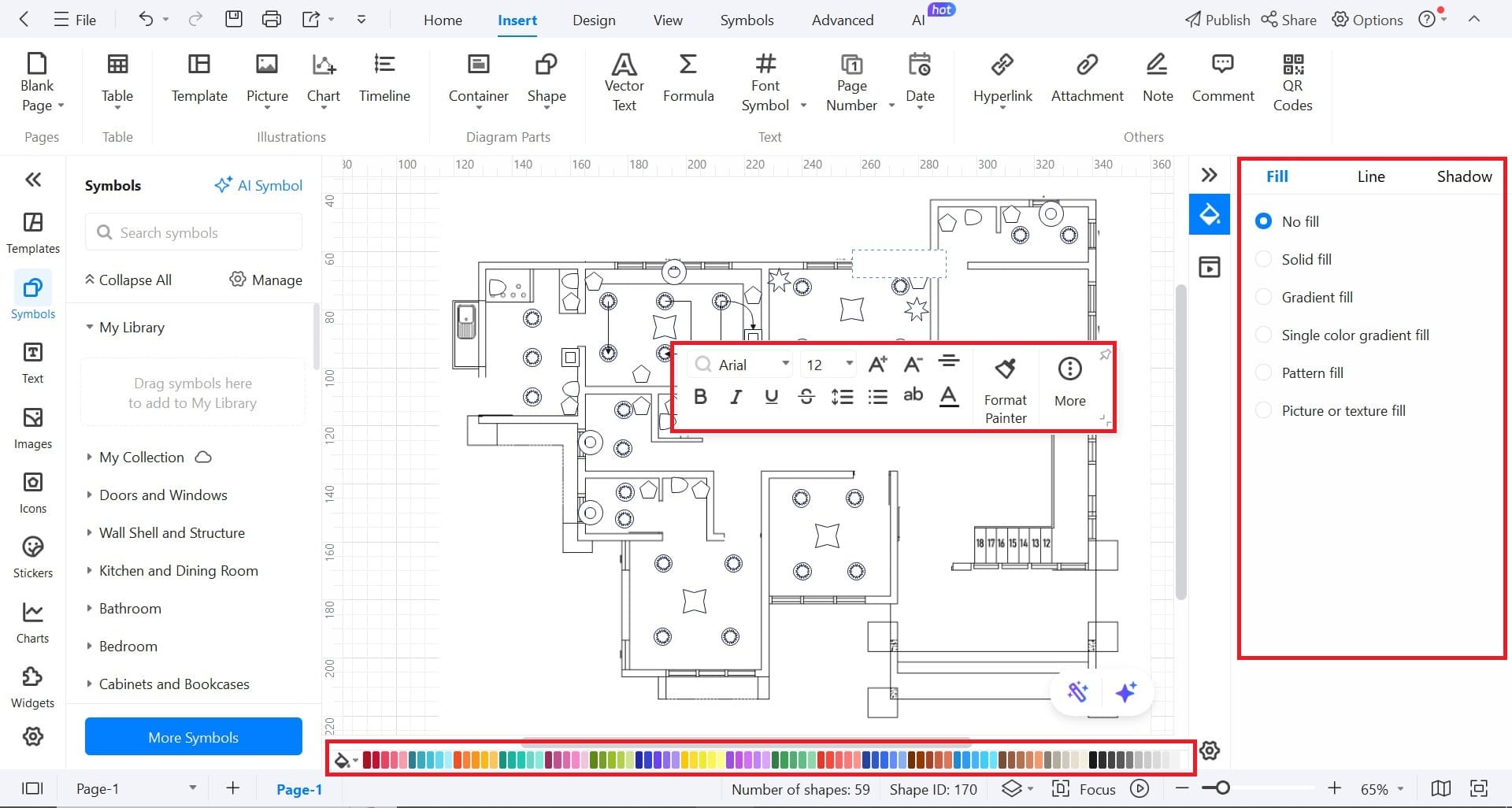
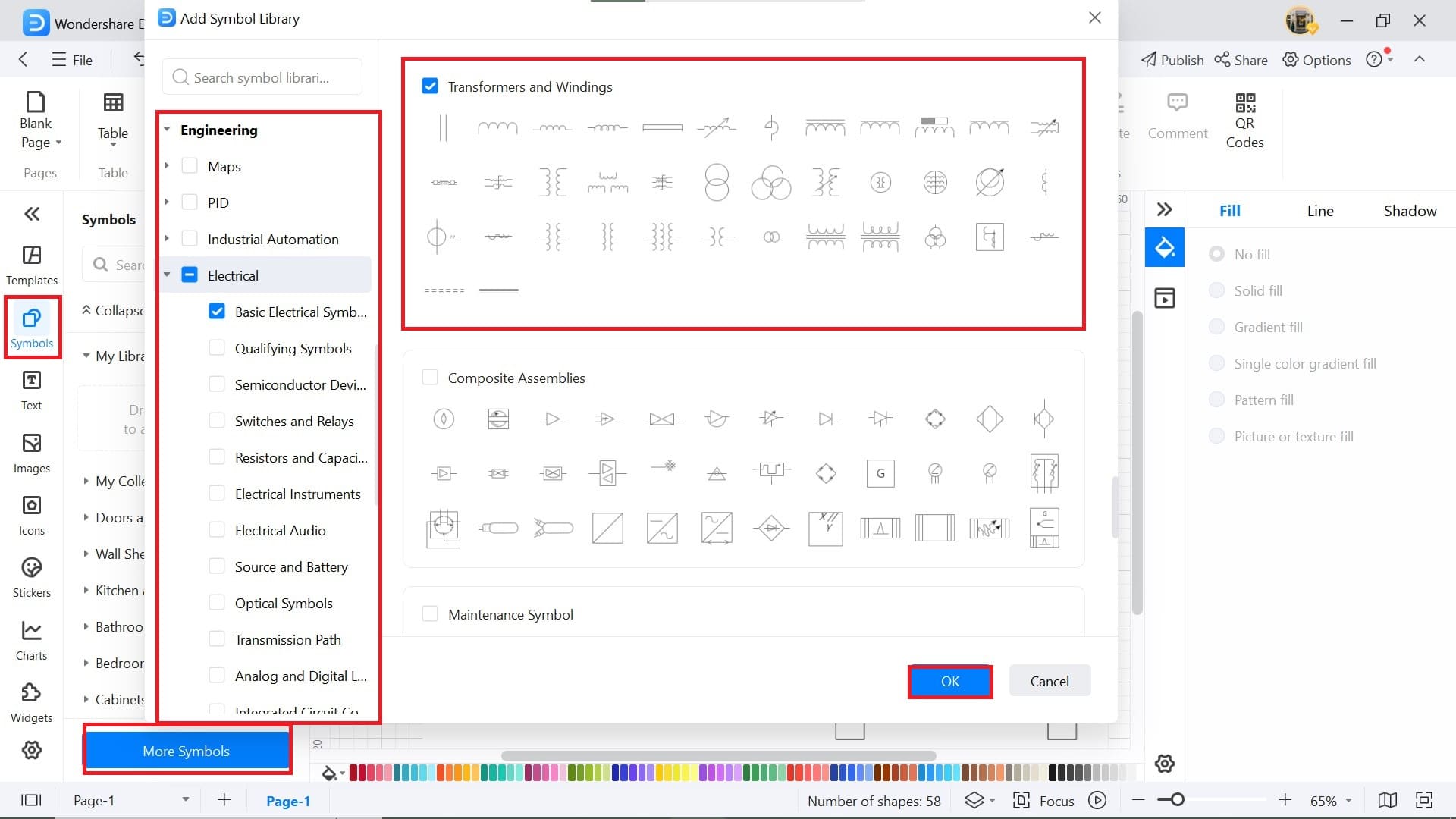
Step4 Access Symbols
- The Symbols panel is present on the left side.
- From here, you can access all the symbols for creating your design.
- To find electrical plan-specific symbols, click More Symbols.
- A new tab of Symbol Library will open. Scroll down a little, Engineering > Electrical > Transformer and Windings.
Step5 Finalize the Drawing
- Once satisfied with the design, you can start downloading.
- EdrawMax has various export options, including JPG, PNG, PDF, PPT, and more.
- Pick your preferred format and save the creation to your device.
- Alternatively, you can save it to the EdrawMax cloud to ensure you never lose it.
Final Notes
Becoming an expert in electrical symbols requires keen focus. Many transformer symbols can easily be mistaken for one another as they have little difference. Misinterpretations can lead to costly mistakes. Knowing these distinctions is essential to ensure each part is correct in a circuit.
Engineers and technicians may be experts in distinguishing them, but for laymen, software like EdrawMax brings unmatched ease. Tools like EdrawMax enable even someone with no experience to create professional electrical plans. Bringing perfection to each project. Moreover, it has an extensive library of electrical transformer symbols. With it, you can say goodbye to complex engineering software. Utilize EdrawMax’ features and accurately create both simple and complex electrical designs on one platform.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ
-
Why are transformer symbols important?
Symbols act as a universal language for engineers, providing standardization. This helps convey information about the transformer’s type and function, regardless of the reader’s tongue. -
What do transformer symbols represent?
Through the transformer symbols, engineers can recognize its functions. The symbols usually represent their physical components, like the number of coils or windings. -
Where can I find a list of electrical symbols?
Online symbol libraries like EdrawMax offer a comprehensive collection of electrical symbols. These can be accessed easily for free. For academic purposes, engineering handbooks can come in handy.






