Are you familiar with class diagrams and UML class diagrams? If not, don't worry—we'll introduce you to class diagrams and guide you through the process of creating your own professional diagrams.
A class diagram serves as a blueprint for creating one or more objects. The Unified Modelling Language (UML) is a standardized modeling language used to visualize system or object designs. UML diagrams are ideal for product design, allowing you to focus on critical aspects like ergonomic design before prototyping. They also form an essential part of project documentation.
What is a Class Diagram?
A class diagram is a static structure used in software engineering that illustrates classes, their attributes, operations, and relationships between them. This visualization helps software engineers develop application code and serves as a documentation tool for describing, visualizing, and documenting various system facets.
Class diagrams are the only UML diagrams that can be directly mapped to object-oriented languages, making them essential for modeling object-oriented systems. They are widely used during the construction phase of object-oriented systems.
These diagrams form the foundation for component and deployment diagrams while describing system responsibilities. They are crucial for application analysis and design, as well as for both forward and reverse engineering processes.
EdrawMax offers numerous professional UML class diagram templates available for free use.
EdrawMax
All-in-One Diagram Software
- Superior file compatibility: Import and export drawings to various file formats, such as Visio
- Cross-platform supported (Windows, Mac, Linux, Web, Android, iOS)
Class Notation
Class diagrams consist of three primary components, as illustrated below:
- Class Name
- Class Attributes
- Class Operations
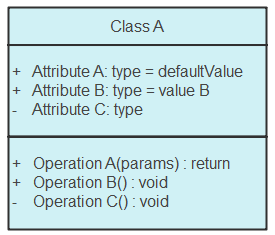
A single rectangle represents each class, divided into three compartments: the top compartment for Class Name, the middle for Attributes, and the bottom for Operations.
Class Name
The class name is crucial for graphical representation and should appear in bold in the top compartment, starting with a capital letter. Abstract classes should be displayed in italics for proper identification.
Attributes
Attributes are listed in the middle compartment, detailing all properties of the modeled object. You can add new attributes or derive them from existing ones. Attributes should be meaningful and typically include visibility factors that describe accessibility levels.
Operations
Operations represent processes that a class can execute, corresponding to class methods. There's no need to display operations that simply mirror attributes, as this information can be deduced from the attribute list.
Class Relationships
Building relationships is the next critical step in class diagram creation. The three primary relationship types include:
- Generalizations
- Associations
- Dependencies
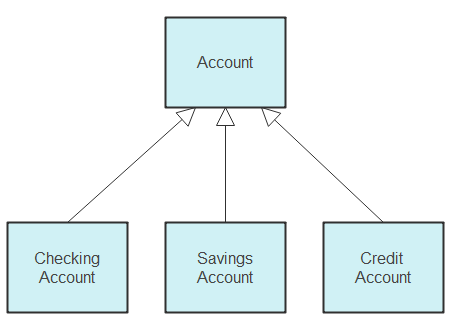
Generalizations
Generalizations, commonly known as Inheritance, connect subclasses to their superclasses. While class diagrams allow subclasses to inherit from multiple superclasses, they cannot model interface implementation. For example, Checking, Savings, and Credit Accounts are generalized by Account.
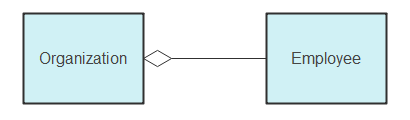
Associations
Association represents a static relationship between two entities. For instance, the association between a student and school is "studies."

The multiplicity factor in associations indicates how many times an attribute is multiplied. If 100 people work at an organization, the attribute multiplies 100 times.
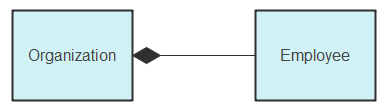
In aggregation, two classes maintain a whole-part relationship. For example, if an employee is absent, the organization continues to function.
Aggregation includes a special type called composition. In composition, classes are so strongly connected that one cannot function without the other. For instance, if an organization closes, all employees must leave.
Dependencies
Dependency indicates that one class depends on another. Changes in one class will affect the dependent class. For example, an employee depends on the organization.
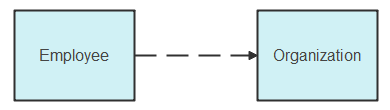
Class Diagram Examples of Common Scenarios
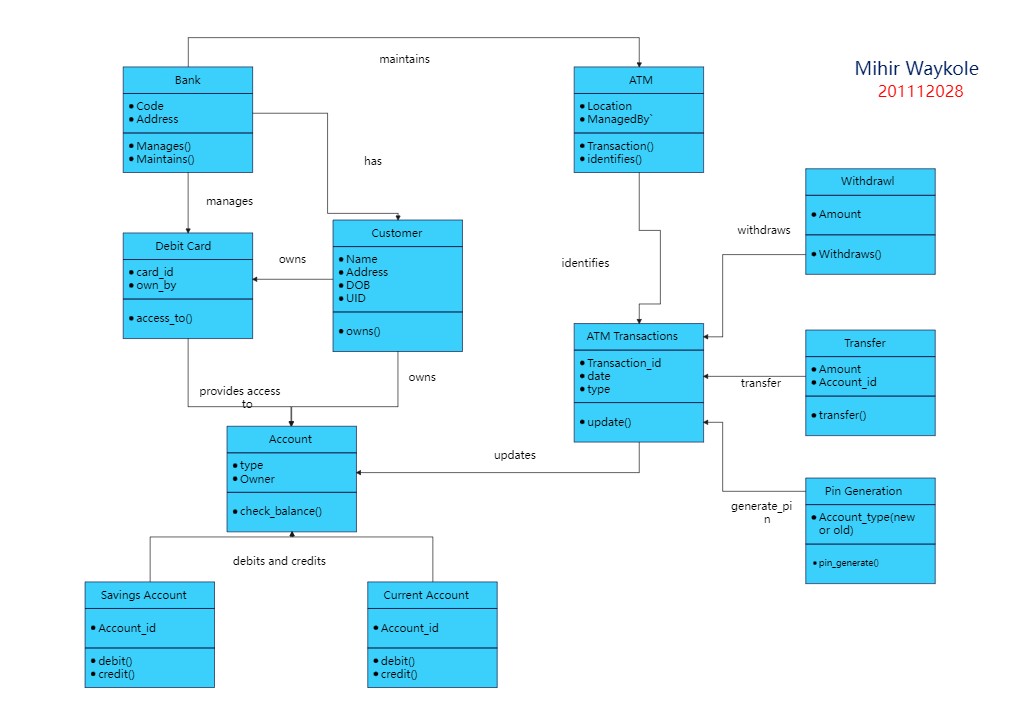
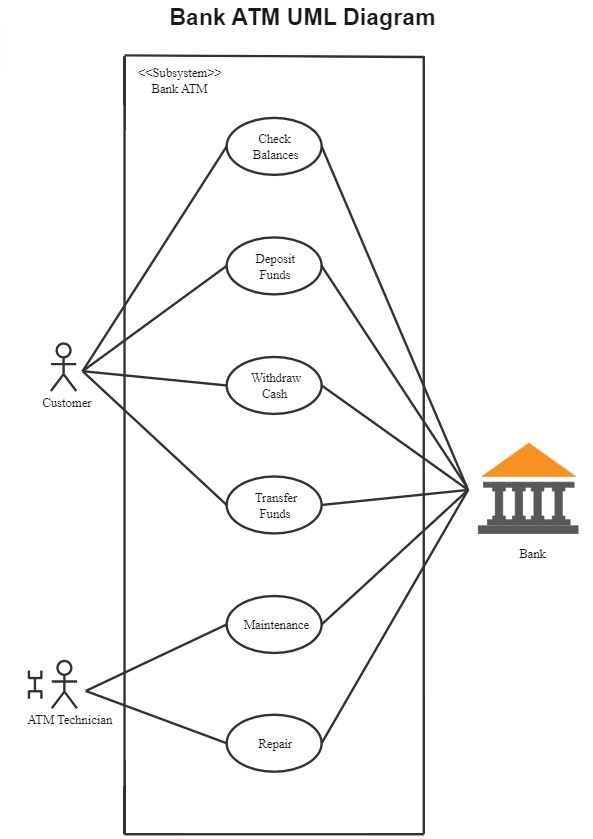
1. Class Diagram for ATM
This ATM class diagram maps the structure and attributes of automated teller machine operations. It demonstrates relationships between multiple classes, providing a comprehensive overview of ATM functionality. Use this template as-is or customize it to meet your specific requirements.
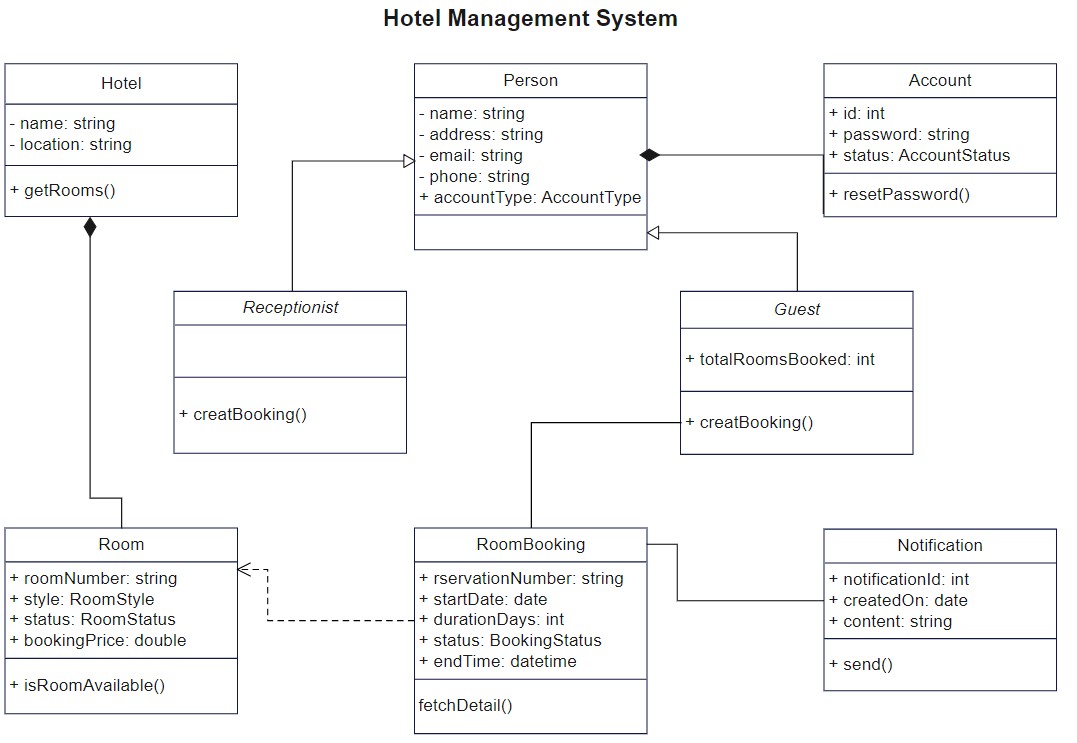
2. Class Diagram for Hotel Management System
This hotel management class diagram meticulously connects all classes through arrows to illustrate their relationships. Easily customize this comprehensive diagram by adding additional classes to match your specific hotel management needs.
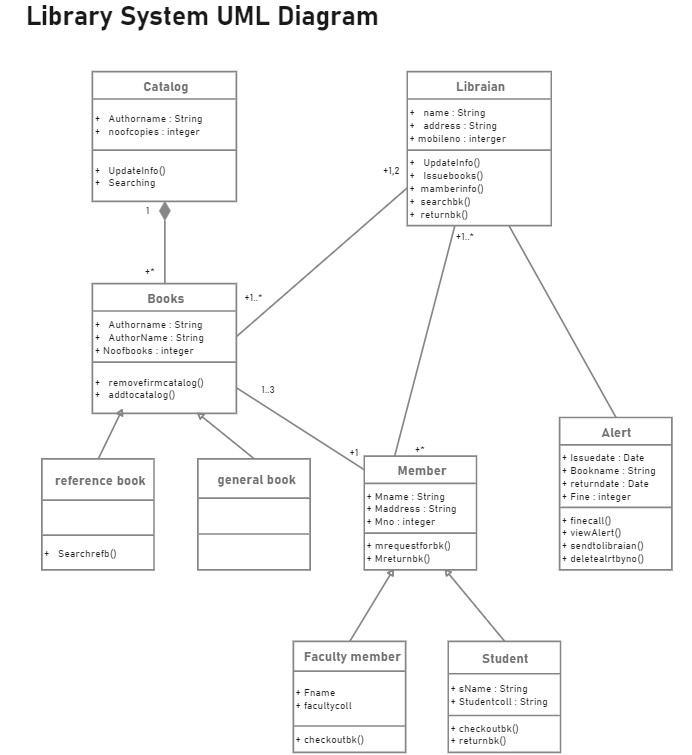
3. Class Diagram for Library Management System
This library management system class diagram features multiple classes including user, librarian, book, and account. It details the attributes and operations of each class while demonstrating their interrelationships within the library management context.
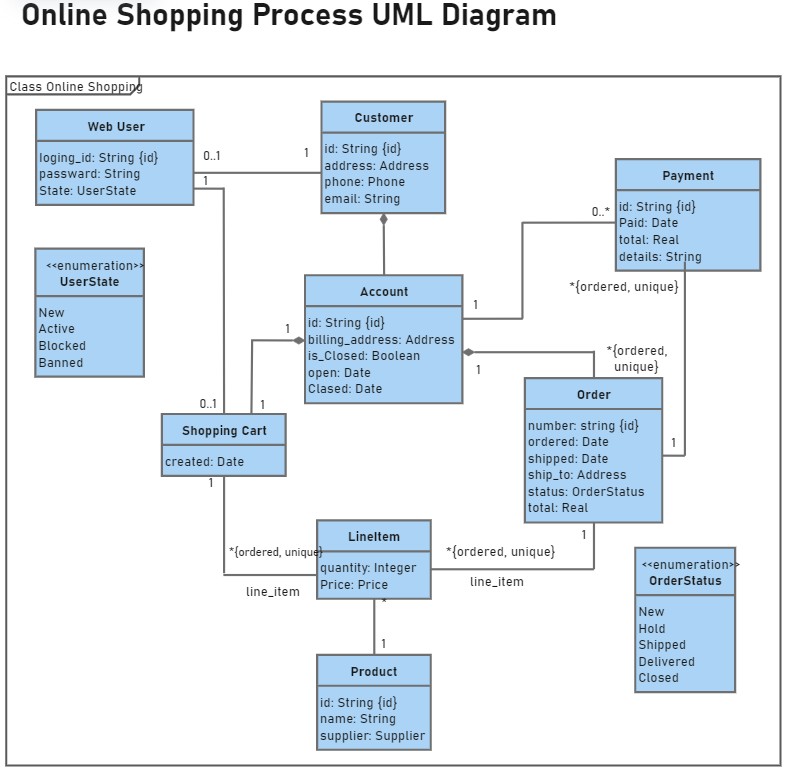
4. Class Diagram for Online Shopping
This online shopping class diagram presents the domain model for e-commerce systems. It clearly illustrates how classes like user and account interact to facilitate order placement and shipment processes, making it accessible for both software engineers and business analysts.
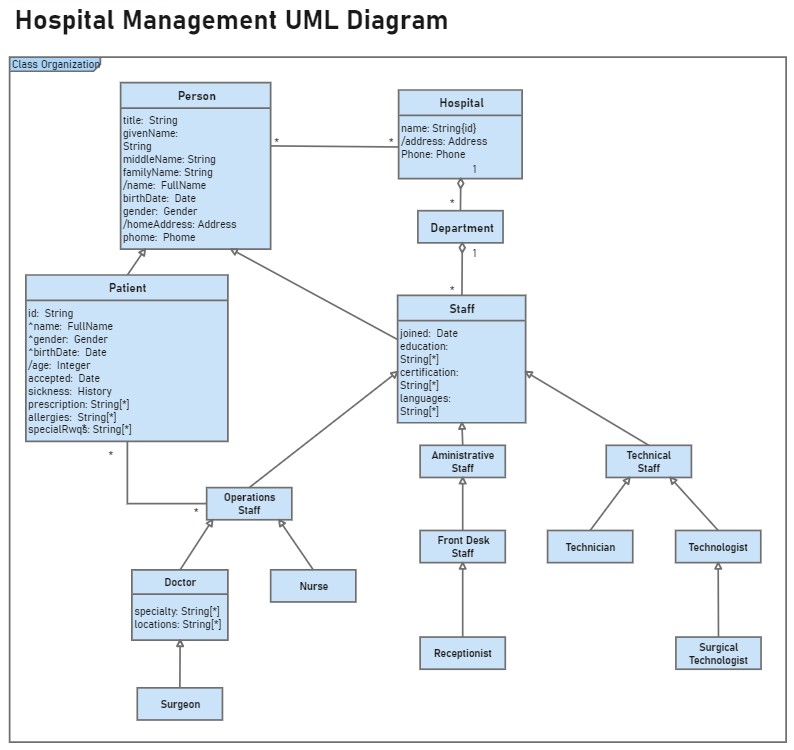
5. Class Diagram for Hospital Management System
This hospital management class diagram template provides an excellent foundation for healthcare system modeling. It demonstrates multiple class diagrams including patient, staff, and treatment classes with their interrelationships, which can be customized to your specific requirements.
6. Class Diagram for Banking System
This banking system class diagram illustrates classes such as banks, ATMs, and customers. Each class displays attributes in the second compartment (for example, a bank's attributes include account number and balance), with clear relationship indicators showing how they interconnect within the financial system.
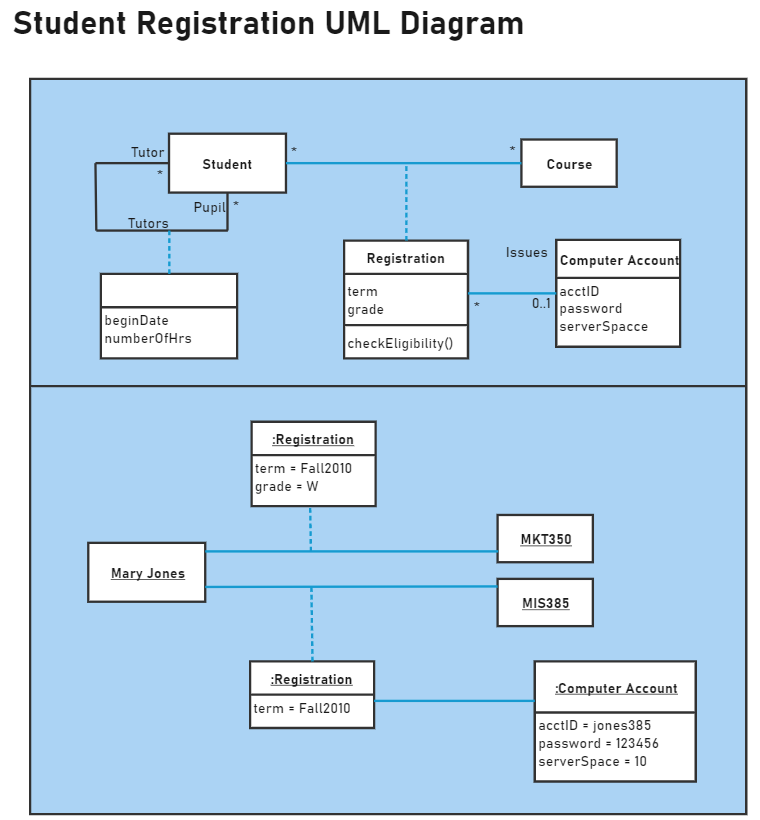
7. Class Diagram for Student Registration System
This student registration class diagram features classes including student, account, course registration manager, and course. Its linear design simplifies understanding, with registration, course, and account as subclasses linked to the registration manager via solid arrows. Easily modify this template by adding new classes to match your registration system's specific architecture.
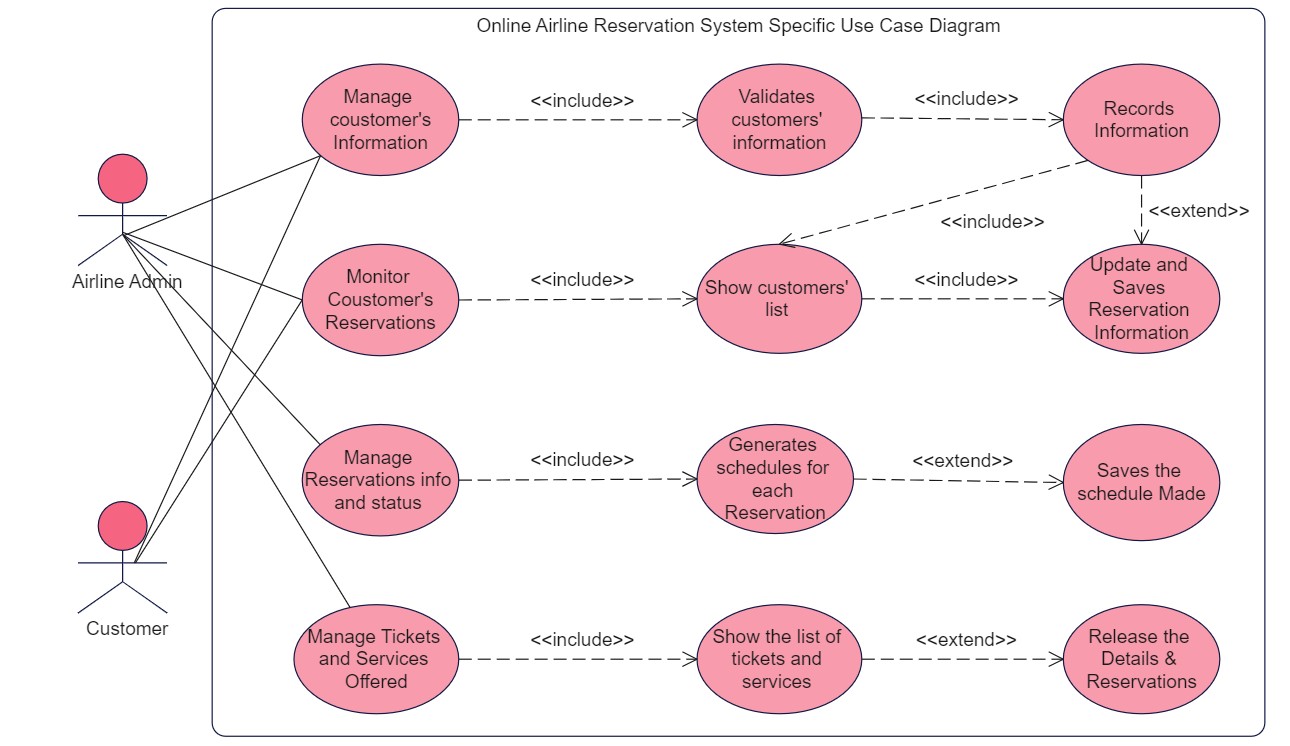
8. Class Diagram for Airline Reservation System
This airline reservation system class diagram template showcases classes, their structures, attributes, operations, and relationships. Primary classes include Reservation, passenger, ticket booking, and employee. The diagram features multiple dependent and aggregate relationships, reflecting the complex interactions between various system components and multiple passengers.
Use EdrawMax for Class Diagram Creation
While class diagrams primarily model system static views, their utility extends much further. These diagrams are essential for constructing executable code through forward or reverse engineering processes. They also serve as excellent foundations for deployment and component diagrams. Selecting appropriate diagrams for each specific scenario remains crucial for effective system modeling.
For both professional engineers and beginners, EdrawMax provides an exceptional platform to create professional class diagrams that enhance documentation and visualize designs. With an extensive library of professional class diagram examples, you can quickly select and customize templates to meet your specific needs. The intuitive interface ensures accessibility for users at all skill levels, enabling efficient and rapid class diagram creation.