LAN Diagram Complete Guide
Ready to Create Your LAN Diagram?
EdrawMax specializes in professional diagramming and visualization. Master LAN diagram creation with our complete guide and start designing with confidence. Download now and try it free!
In computing, a network connects two or more devices to enable electronic communication, file exchange, and resource sharing. While various network types like MANs and WANs facilitate information exchange between connected computers and devices, Local Area Networks (LANs) remain the most commonly used in IT environments. Since LAN networks—particularly in large organizations—involve multiple interconnected computers and devices, IT specialists rely on LAN diagrams to visually plan network architecture before implementation.
Clear visualization of LAN network components becomes critical during emergencies or communication failures. With a detailed LAN diagram, IT professionals can quickly pinpoint issues and implement solutions. Various tools are available for creating LAN diagrams, with EdrawMax standing out as a user-friendly, free network diagram solution used by millions worldwide. It offers over 2600 symbols and 1500 pre-made templates. This article provides an in-depth look at LAN networks, LAN diagrams, and how to create them efficiently using EdrawMax.
1. What is a Local Area Network (LAN)
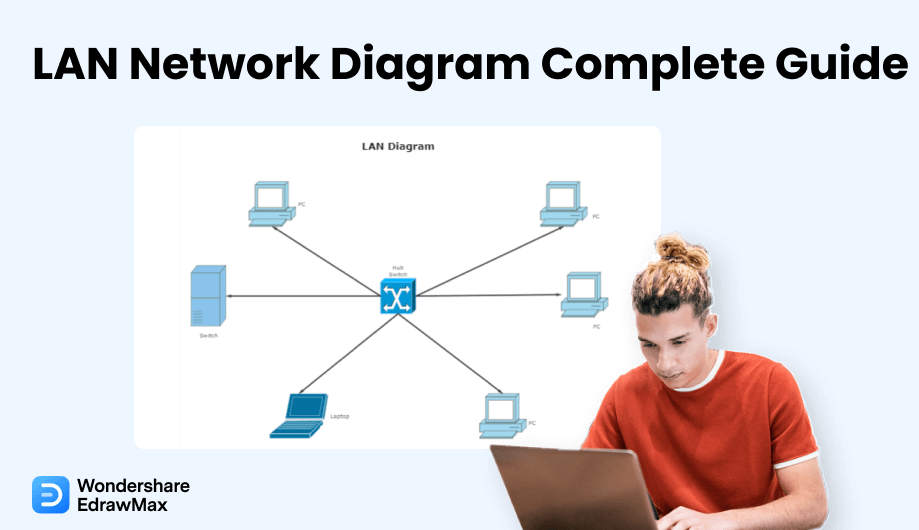
A local area network (LAN) consists of devices such as computers and peripherals connected to a central server via WiFi or Ethernet cables. The main server housing these devices is located in a specific physical location, which could be a home, office, or entire building, depending on the network's size.
Local area networks range from simple setups with a single computer and peripherals in a home environment to complex networks with numerous computers and devices managed by multiple users in large organizations.
A LAN diagram provides a visual representation of how different network components (nodes) are arranged and interconnected. LAN diagrams feature two types of topologies: physical and logical. The physical topology shows all devices within the network, including switches, routers, and computers. The logical topology illustrates how data travels between different nodes in the LAN network.
A LAN diagram serves as an architectural blueprint or map of a LAN network. IT professionals use these diagrams to plan network layouts, visualize node connections, and understand data exchange patterns within the network.
1.1 What is the Local Area Network (LAN) Used for
LANs primarily facilitate easy information access within the network. Users can access data from any connected computer or device. For example, in a school LAN network, users can retrieve information from any school computer connected to the network without physically accessing the specific device containing the data.
Secondly, LANs enable efficient file exchange, making collaborative work significantly easier. Team members can create documents on their computers and share them instantly with other network users without emailing or faxing files individually. This capability extends to resource sharing, allowing users to send print jobs to network-connected printers without physical movement. These features make LANs particularly valuable for both individuals and businesses.
1.2 Types of LANs
Client-Server LAN
Client-Server LAN networks connect multiple client devices to a central server via cables or wireless connections. The server manages critical functions including network traffic management, file access, application access, security, and authentication.
Clients can perform tasks with each other or access internet resources through the server, which is pre-programmed to handle database access, email, document sharing, printing, and other services. Network administrators control file permissions, determining which clients can read or write files. Client-server LANs are commonly used in schools, offices, and industrial settings.
Peer-To-Peer LAN
Peer-to-Peer LANs operate without a central server, making them smaller in both size and bandwidth capacity. All devices connect directly to each other and perform network functions collectively. This LAN type is ideal for homes and small environments where server infrastructure is unnecessary.
2. Pros and Cons of Local Area Network (LAN)
Like all network types, LAN networks present both advantages and disadvantages. Below we examine the key benefits and limitations of implementing LAN technology.
Pros of LANs:
-
Cost efficiency: LAN networks significantly reduce expenses for individuals and businesses. Rather than purchasing individual software licenses for each user (including text editors, video editing software, antivirus protection, and cloud storage), organizations can purchase single licenses accessible to all network users. This approach can save thousands of dollars monthly on software expenses.
-
Effortless file sharing: LAN networks enable seamless access and sharing of various file types including text, audio, and video files. Users can send and receive files between any computers within the network environment.
-
Resource sharing capability: Beyond file sharing, LAN networks allow shared access to peripherals including scanners, printers, modems, and hard drives. All connected computers can access these resources without requiring individual devices for each user, reducing hardware costs without compromising performance.
-
Rapid communication: LANs facilitate quick exchange of messages, data, and files between departments and team members. This eliminates the need for physical movement between offices when collaboration is required.
-
Centralized access management: Centralized data storage accelerates operations and saves time. Files created on one computer become accessible to all network users, who can view, edit, share, and print documents as needed.
-
Enhanced security: LAN networks are less vulnerable to external hacking attempts since all computers reside on a local server. Network hosts can grant or revoke user access, providing additional security layers for stored data.
Cons of LANs:
-
Initial installation cost: While LANs reduce software and resource expenses, they require significant upfront investment in hardware (modems, switches) and specialized software. Maintenance costs also apply, as networks require dedicated administrators to monitor for potential issues that could become costly if undetected.
-
Server vulnerability: The centralized data access that makes LANs convenient also creates vulnerability. If the main server crashes, all connected computers lose access to stored data, potentially disrupting operations.
-
Security software requirements: Devices require firewall activation and antivirus protection since data transmitted through internet connections can be accessed and modified by hackers attempting to install malware.
-
Limited coverage area: LANs are designed for limited geographical coverage (typically under 10 km) within buildings, schools, or homes. Users cannot access data beyond this range due to structural limitations of both wired and wireless connections.
-
Security and privacy risks: While LANs are less susceptible to external attacks, internal security glitches can allow unauthorized data access. Network administrators have access to all user data, including browsing history and downloads, creating potential privacy concerns depending on how administrative privileges are exercised.
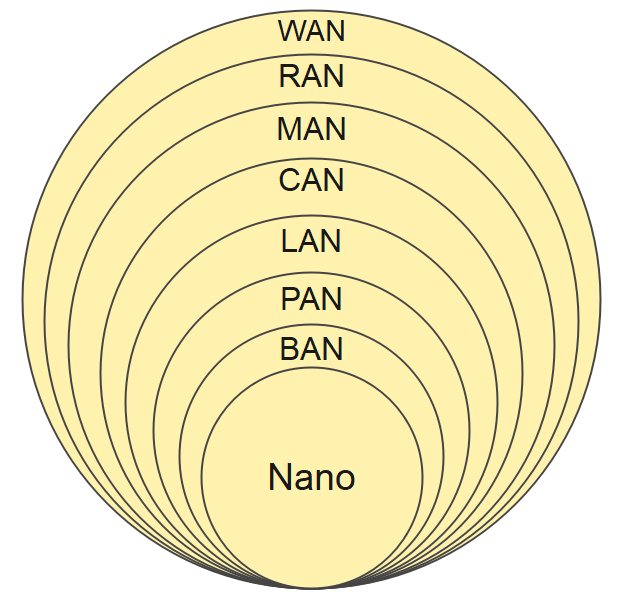
3. Differences Between LAN, MAN, and WAN
Several key differences distinguish LANs, WANs, and MANs. The most obvious distinction is geographical coverage capacity.
LANs typically serve small areas like schools, homes, or small offices, while MANs can span entire cities and multiple buildings. WANs have no geographical limitations, covering countries and continents. Consequently, LAN, MAN, and WAN diagram creation processes differ significantly, with MAN and WAN diagrams being substantially more complex than LAN diagrams.
Connection methods represent another distinguishing factor. LANs typically use Ethernet or wireless connections, while MANs primarily rely on cables. WANs mostly utilize leased telecommunication circuits for connectivity.
Information transmission speed constitutes the third major difference. LANs outperform other network types in information and file exchange speed due to their limited geographical coverage, resulting in faster internet connections compared to MANs and WANs.
3.1 LAN (Local Area Network)
LANs can include desktop computers, laptops, printers, WiFi modems, servers, routers, and switches connecting multiple LANs. Ethernet cables typically connect all devices within a LAN. While designed for small areas like homes, offices, and schools, LAN size can vary significantly depending on how many networks are interconnected.
- Limited geographical coverage
- Ethernet or WiFi connectivity
- High-speed internet connection
3.2 MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
MAN (metropolitan area network) connects computers and resources across larger geographical areas ranging from 50-60 km. MANs typically consist of multiple interconnected LANs serving groups of buildings, towns, or cities. They represent an intermediate scale between LANs and WANs.
- Covers cities, buildings, and towns
- Modem and cable connectivity
- Medium-speed internet connection
3.3 WAN (Wide Area Network)
WAN (wide area network) refers to telecommunications networks primarily used by organizations to interconnect globally distributed offices, providing staff access to centralized data hubs. While MANs cover cities and towns, WANs operate on a much larger scale, spanning countries and continents. Privately-owned WANs involve substantial costs, though multiple organizations often share ownership. Publicly-accessed WANs include the internet.
- Covers countries and continents
- Uses leased line connections
- Slower internet connection speeds
4. How Does a Local Area Network Work
LAN operation follows these fundamental steps:
Step 1: Network component installation
Computers, peripherals, routers, and switches are installed according to a pre-designed LAN diagram.
Step 2: Central computer connection
The main computer connects to the internet via a router, with additional network switches added based on LAN size requirements.
Step 3: Device interconnection
Network devices connect wirelessly or via Ethernet cables. Internet access distributes from the main computer to all connected devices, enabling message exchange, file sharing, and data access across the network.
5. How to Draw a LAN Diagram in EdrawMax
EdrawMax provides a comprehensive diagramming solution for creating LAN network diagrams and various other diagram types effortlessly. It features specialized symbols including mainframe, terminal, cloud, firewall, communication links, printer, switch, server, router, bridge, and hub components. These symbols simplify visualization of diverse LAN network configurations. While multiple methods exist for creating LAN network diagrams, EdrawMax offers the most efficient approach with automated features that generate professional LAN diagrams within minutes.
Step1 Open EdrawMax and Login
Begin by installing EdrawMax on your system. Visit EdrawMax Download and select the appropriate version for your operating system. For remote team collaboration, access EdrawMax Online and log in using your registered email credentials.
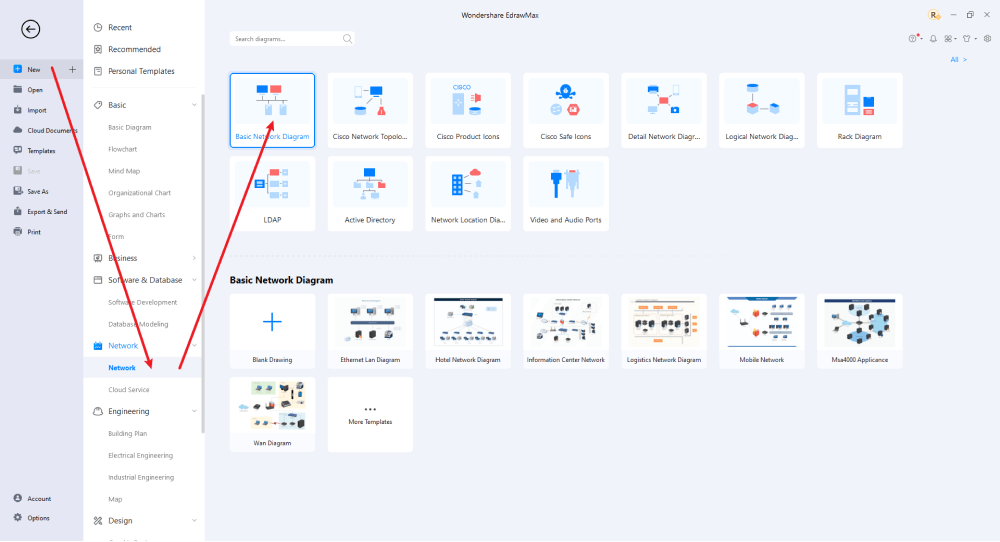
Step2 Select a Template
After launching, the Home screen appears by default. Use the Template bar search box to find LAN Network Diagrams. Built-in templates specific to your search will display. EdrawMax features an extensive template library with over 25 million registered users contributing to the comprehensive Templates Community. Select your preferred template and click Use Immediately to open it in a new customization window.
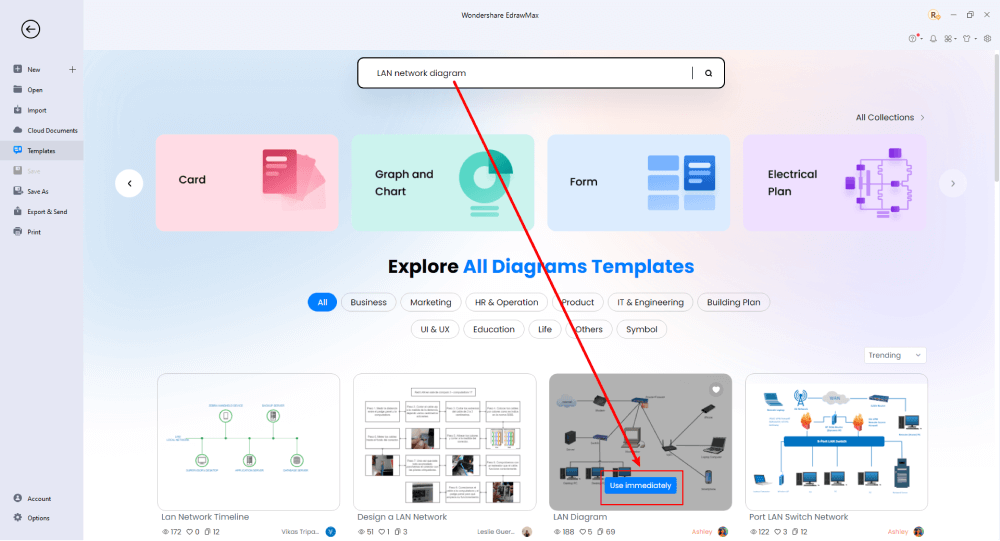
Step3 Create From Scratch
From the EdrawMax homepage, click the '+' sign to access the canvas board for designing LAN network diagrams from scratch. Combine your technical expertise with EdrawMax's extensive symbol library to create detailed network diagrams.
Step4 Select Symbols
EdrawMax includes extensive symbol libraries with over 26,000 vector-enabled symbols for creating any diagram type. If required symbols are unavailable, easily import images/icons or create custom shapes saved for future use. Access the 'Symbols' section from the top toolbar and select 'Predefined Symbol' to explore hundreds of symbol categories for your LAN network diagram.
Step5 Add Components
After sketching basic elements, customize fonts, colors, and other details using the right or top menu to enhance your LAN network design's visual appeal. Draw inspiration from other Templates Community layouts and incorporate suitable images or features into your design.
Step6 Finalize the Plan
Once your LAN network diagram is complete, collaborate with team members using Cloud-based files. EdrawMax provides up to 100MB free cloud storage supporting multiple formats including HTML, PDF, Graphics, Visio, and Microsoft Office. Creating LAN network diagrams in EdrawMax involves a straightforward process of selecting templates and customizing them to meet specific design requirements, with numerous professionally-designed templates available for organizational use.
Creating LAN network diagrams in EdrawMax is fundamentally simple: select templates and customize them while dragging and dropping professional network diagram symbols to enhance your plans. For additional guidance, access tutorial videos on our YouTube channel.
6. Local Area Network Examples
EdrawMax provides comprehensive Local Area Network examples and templates. Click images to download EdrawMax and corresponding templates, then customize as needed. Alternatively, access templates from the EdrawMax Templates Community and duplicate them for use.
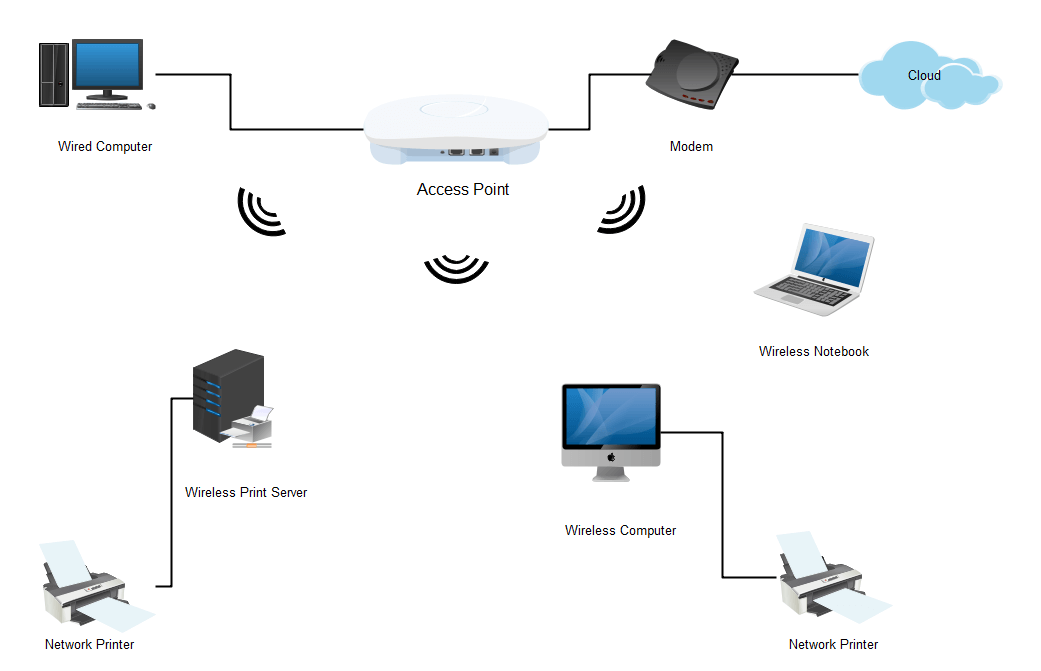
Example 1: Wireless Local Area Network
Wireless Local Area Networks connect two or more computers without Ethernet cables.
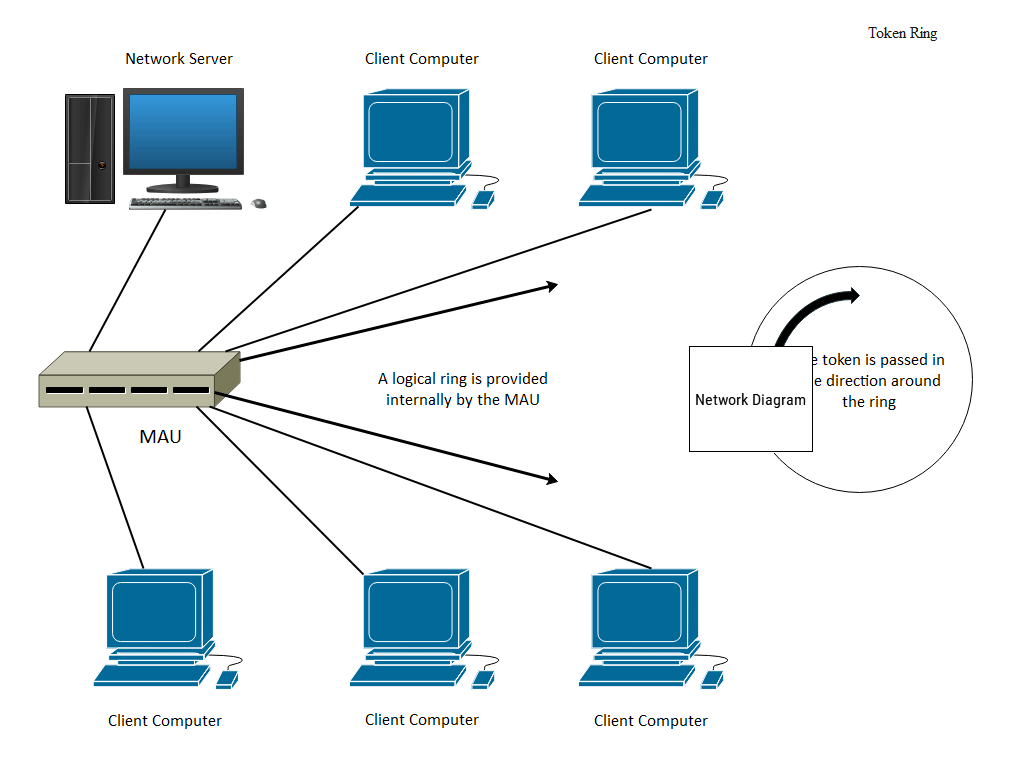
Example 2: Token Ring Network
Token Ring technology represents one of the earliest LAN implementations, initially used by IBM staff in the late 1990s. Token Ring Networks connect multiple workstations to a token—a three-byte frame functioning as channel access—that circulates among workstations in logical, ring-like motion. Token Ring Networks have been largely replaced by Ethernet technology in contemporary applications.
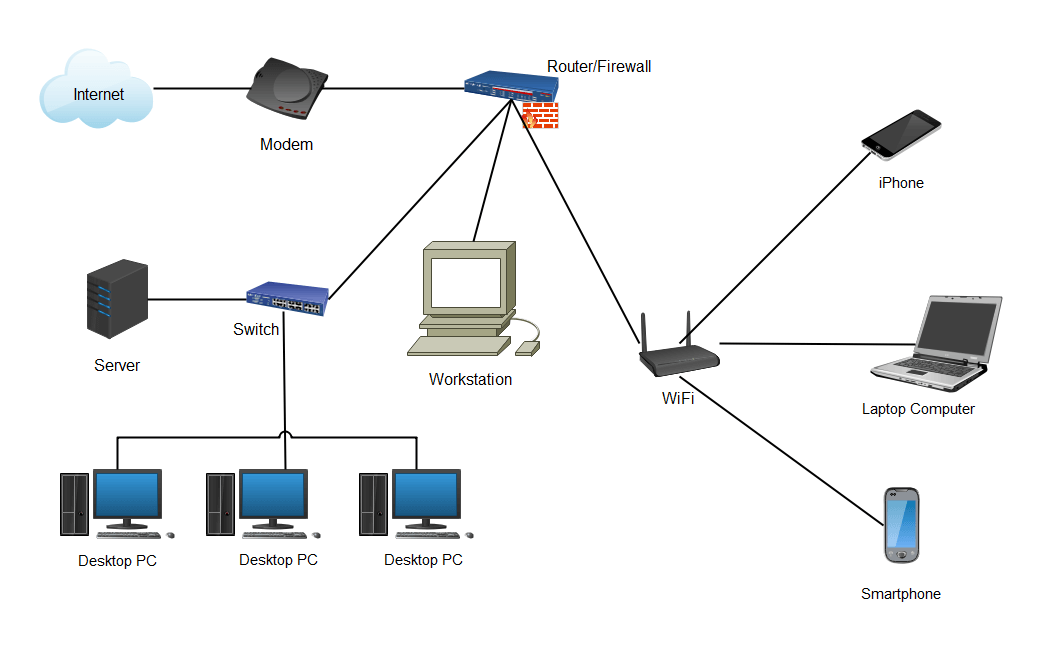
Example 3: Local Area Network Diagram
Local area network diagrams serve as mapping tools that IT specialists use to organize LANs before implementation. These visual representations depict LAN components, their interconnections, and information exchange patterns. While seemingly unnecessary to casual users, LAN diagrams provide critical value to IT specialists—serving as visual guides during network setup and troubleshooting future network issues. Among various LAN examples, wireless LANs represent the most commonly implemented variant, appearing in virtually all contemporary LAN installations.
7. Free Network Diagram Tool
Creating LAN diagrams manually presents significant challenges, making diagramming tools essential for regular network diagram creation. While numerous free network diagram tools exist, most contain substantial limitations. For professional-quality, clear network diagrams available at no cost, we strongly recommend EdrawMax. The exceptional network diagram software becomes essential for frequent network diagram creation. Despite many freely available options, most contain significant shortcomings. EdrawMax delivers professionally-designed, clear network diagrams without cost barriers.
Key advantages of choosing EdrawMax for network diagram projects:
- User-Friendly Interface: EdrawMax simplifies network diagram creation through pre-made shapes and automatic floating buttons, saving time while maintaining efficiency. The interface remains simple, smart, and intuitive throughout the design process.
- Extensive Symbol Library & Templates: Standardized, polished network diagram symbols ensure accurate, presentation-quality results. EdrawMax includes thousands of network diagram symbols organized into 30 separate libraries, with options to load needed libraries and close unnecessary ones. Personalization tools allow custom symbol creation and modification.
- Editable Export Formats: EdrawMax's powerful network diagram software exports created files into most common formats while maintaining editability and shareability—unlike other tools that export uneditable files, making EdrawMax uniquely valuable.
- Cross-Platform Availability: EdrawMax functions as a powerful, fast, and user-friendly network diagram solution across Mac, Windows, Linux, and online platforms. It enables home network layouts, Cisco networks, WAN networks, AWS networks, and other network visualizations with premium-quality symbols at accessible pricing, earning recognition as the ultimate network diagram solution.
8. Final Thoughts
In summary, a LAN represents a network where two or more computers and peripherals interconnect via wireless or cable connections. LAN networks see widespread use today, particularly in medium-sized environments like homes, schools, and small offices. Proper LAN operation requires accurate component placement within the system, achieved through detailed planning using LAN diagrams. These visual maps represent different devices within LAN networks and their interconnections.
EdrawMax serves as a free diagramming tool used by hundreds of thousands of network designers and IT specialists to accurately visualize LAN components and their information exchange patterns. It represents a highly recommended solution for network designers, offering hundreds of templates, network-specific graphic resources, and unique features unavailable elsewhere.
Network Diagram Complete Guide
Explore our comprehensive guide covering network diagram types, symbols, and creation techniques to master network diagramming.





